Are you looking to enhance your productivity by limiting distractions or strengthen your computer's security by blocking certain websites on Windows? Dive into the world of website blocking with our guide on how to block websites in Windows using the host file. Today, more than ever, managing online content access is crucial, and we are here to walk you through a powerful method that puts you in charge.
How to Block Websites in Windows Using Host File
In this tech-savvy article tailored for enthusiasts and website administrators, we unravel the significance of restricting access to specific websites within a Windows environment. Discover how the host file method serves as a robust tool in your arsenal – a method that empowers you to directly influence which sites can be accessed on your system.

Let's embark on a journey together where you learn not just about blocking websites but also about taking command of your digital space like never before. Get ready to harness the potential that lies within your reach.
Understanding Website Blocking in Windows
Website blocking on Windows is a powerful tool with multiple applications. It serves different purposes, from enhancing productivity to bolstering security. For instance, parents often block certain websites to shield their children from inappropriate content. In a work setting, companies may restrict access to social media sites to maintain focus and prevent data breaches. Understanding website blocking's versatility allows users to tailor it to meet their specific needs effectively.
When it comes to productivity, blocking distracting websites can significantly boost efficiency. Imagine working on an important project without the temptation of mindlessly scrolling through social media feeds or watching videos online. By imposing these digital barriers through website blocking, individuals can stay better focused and accomplish tasks more quickly. Additionally, from a security standpoint, preventing access to malicious or phishing websites helps safeguard sensitive information and prevents potential cyber threats.
To begin your journey in website blocking on Windows using the host file method, first acquaint yourself with accessing this crucial file within the operating system. The host file acts as a manual DNS where you can manually map IP addresses to domain names. By editing this file, you can dictate which websites are accessible on your system.
With a step-by-step guide on how to find and modify the host file effectively, you'll be equipped with the knowledge needed to implement tailored website restrictions on your Windows device for improved productivity and enhanced security measures.
Locating and Editing the Host File
To begin blocking websites through the host file in Windows, you first need to locate it. The host file can typically be found in the ‘etc’ directory within the system files.
For Windows users, the path is usually ‘C:WindowsSystem32driversetc.‘ Accessing this file requires administrative permissions due to its integral role in directing network connections. To edit the host file, you must open it with a text editor like Notepad or Notepad++.
Administrator permissions are crucial when editing the host file because this system file directly impacts how your computer connects to websites. Without proper permissions, changes made to the host file may not save or take effect. By right-clicking on your text editor and selecting ‘Run as Administrator,’ you ensure that your modifications will be implemented successfully.
When editing the host file, errors can sometimes occur, leading to unexpected outcomes such as network connection problems or incorrect website redirects. It's essential to double-check each modification added to avoid syntax errors or misplaced entries that could unintentionally block desired sites or interfere with system functions. Being cautious while making changes and following formatting guidelines precisely can prevent these issues from arising during the website-blocking process.
By understanding how to find and modify the host file in Windows, users gain more control over their browsing experience and can enhance productivity by blocking distracting websites efficiently. Remember, taking precautions like creating a backup of the original host file before alterations and verifying changes afterward will help ensure a seamless website-blocking process without encountering unnecessary hurdles.
Adding Websites to Block List
When it comes to adding websites to the block list in the host file, precision is key. Start by opening the host file you located in the previous step and make sure you have administrative privileges. The host file may appear intimidating at first glance, but with a few simple rules, you can effectively block specific websites. It’s essential to maintain proper formatting when adding URLs, as even a small error can lead to unintended consequences.
For example, let's say you want to block access to social media sites like Facebook on your Windows computer. Begin by entering “127.0.0.1” followed by a space and then the URL of the website you wish to block. In this case, it would look like “127.0.0.1 www.facebook.com”. Ensure that each entry is placed on a new line for clarity and accuracy in blocking websites effectively.
To avoid unexpected issues or errors, always back up your original host file before making any changes. This precautionary step ensures that if something goes wrong during the editing process, you can easily revert to the unaltered version of the host file without losing important system settings or configurations. Remember, taking these extra measures can save you time and frustration in case of any mishaps along the way.
In summary, properly formatting entries in the host file and double-checking for accuracy are fundamental when adding websites to your block list in Windows. By creating backups before modifications, you safeguard against potential complications and maintain the integrity of your system files during website blocking procedures. These best practices not only enhance efficiency but also provide peace of mind as you take control of your browsing experience on Windows platforms.
Install the BlockSite Chrome Extension
To effectively restrict access to certain websites, utilizing a Chrome extension is recommended. A well-known option in this category is Block Site. To install it, navigate to the extension's download page and click on “Add to Chrome,” then “Add extension.” Allow the installation process to complete.
Install Block Site Microsoft Edge Extension
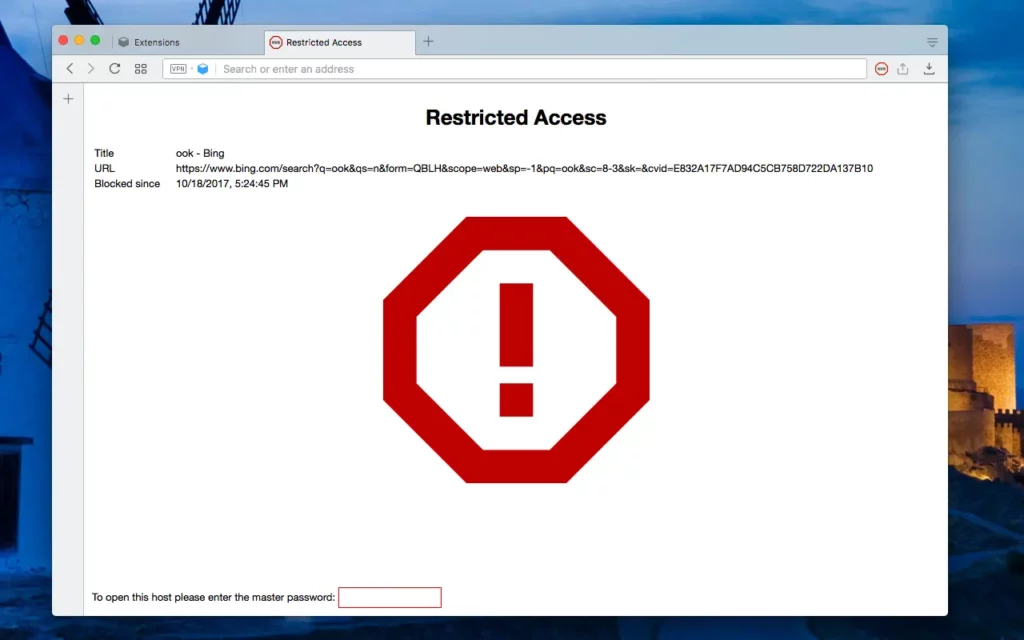
This browser extension offers a convenient solution for users who wish to control and manage their online experience by blocking access to specific websites. The extension's settings and customization options are safeguarded by a master password, ensuring that only authorized users can modify the list of blocked sites or access the restricted content.
An additional feature of this extension is its ability to redirect navigation from one particular website to a different, user-specified webpage. This can be particularly useful in various scenarios, such as when a user wants to automatically open a preferred alternative site instead of the original one, or when a website is under maintenance and users need to be directed to a temporary page.
Overall, this extension provides an efficient and adaptable method for managing and filtering website access, with an emphasis on user control and convenience.
Testing and Verifying Blocked Websites
Once you have added websites to your block list in the host file, it is crucial to test whether the changes were successful. To verify if a website has been effectively blocked using the edited host file, simply open a web browser and type in the URL of the site you intend to block. If the page loads normally, your blocking attempts may not have been successful.
Common issues that may arise when verifying blocked websites include typographical errors in the host file entries or incorrect formatting. It's essential to double-check each entry for accuracy, ensuring there are no extra spaces or missing characters. Additionally, be mindful of any cached DNS records on your system that could override your block settings. Clearing your browser cache after editing the host file can help prevent these conflicts.
Remember that testing and verifying blocked websites should be done across different browsers to ensure consistent results. Sometimes certain browsers may ignore changes made to the host file until they are restarted or refreshed. By being thorough in your testing process, you can confirm that unwanted websites are successfully inaccessible across various platforms.
Overall, it's important to understand that troubleshooting is part of the website blocking process. If you encounter difficulties while trying to access blocked sites even after making changes to the host file, revisit your entries for accuracy and look out for any conflicting settings. Verification is key to ensuring that your efforts to block specific websites on Windows using the host file have been carried out effectively.
Advanced Techniques for Website Blocking
While editing the host file is a powerful method for blocking websites on Windows, advanced users may seek more comprehensive solutions. Third-party software offers a robust approach to website filtering, allowing users to implement specific restrictions and access controls with greater ease. Programs like Cold Turkey or Net Nanny provide advanced features such as scheduling blocks, setting up multiple user profiles, and detailed logging of internet activity. These tools not only block websites but also offer insights into browsing habits for better monitoring.
Another sophisticated way to control website access in Windows is through utilizing parental controls or firewall settings. Parental control features built into Windows allow parents to manage their children's internet usage by setting restrictions on particular websites or overall screen time. Firewall settings can be configured to block certain web addresses across all devices connected to a network, providing a centralized approach to website blocking. By tapping into these native features of Windows, users can create broader restrictions tailored to their specific needs.
For example, let's say a parent wants to prevent their child from accessing social media platforms during study hours. By utilizing third-party software like Qustodio or leveraging the built-in parental controls in Windows 10, they can establish time limits and content filters easily. Similarly, a business concerned about data security may opt for firewall-based website blocking to restrict access to potentially harmful sites across all company devices uniformly.
In conclusion, while the host file method remains effective for many users looking to block websites on Windows, exploring advanced techniques offers more sophisticated and tailored solutions based on individual requirements. Whether it's through specialized software applications or leveraging system-level controls like firewalls and parental settings, users can enhance their website blocking capabilities for improved productivity and security. When selecting an advanced technique, consider factors such as user interface preferences, level of customization needed, and compatibility with existing systems for optimal results.
Wrapping Up
From leveraging the host file method to utilizing advanced techniques such as third-party software or parental controls, blocking websites in Windows opens a realm of possibilities for enhancing productivity and safeguarding digital environments. By summarizing the benefits of website blocking through various methods, users can tailor their approach based on specific needs and technical acumen. Whether it's eliminating distractions during work hours or creating a safer browsing experience for children, understanding website blocking empowers individuals to take charge of their online activities.
When considering which technique to employ, it's vital for readers to assess their comfort level with technology and the depth of control they seek over web access. For those well-versed in computer systems, exploring advanced methods like firewall settings may offer a more comprehensive solution than basic host file editing. On the other hand, beginners might find starting with host file modifications a manageable entry point towards efficient website blocking. The beauty lies in the versatility each method provides, catering to a diverse audience with varying expertise levels.
As we conclude this guide on website blocking in Windows, it is crucial to emphasize that experimentation and fine-tuning are key elements in finding an optimal solution. It is not only about restricting access but also about fostering a balanced digital lifestyle and ensuring online safety.
By staying informed about different approaches available – be it through manual configurations or specialized tools – readers can navigate the vast landscape of website blocking confidently and effectively. Ultimately, taking control means equipping oneself with knowledge and tools to shape a digital environment that aligns with individual goals and priorities.
Empower Your Windows Experience with Website Blocking
In conclusion, mastering the art of website blocking on Windows through the host file method can revolutionize your digital experience. Whether you're seeking to enhance productivity, tighten security measures, or manage internet usage for others, knowing how to control access to specific websites is a valuable skill. By harnessing the power of the host file, you can take charge of what content is accessible on your devices with precision and ease.
As technology continues to evolve, having a toolbox filled with techniques like editing the host file in Windows ensures that you can tailor your browsing experience to match your needs. However, remember that with great power comes great responsibility – always proceed with caution and back up files before making changes. Stay curious and continue exploring additional methods for website blocking in Windows to further customize and optimize your online environment.
FAQs:
1. Can I block multiple websites using the host file method?
– Yes, you can block multiple websites by adding separate entry lines for each URL following the same format shown in the guide.
2. Will blocking a website affect other users on my computer?
– No, blocking a website using the host file will only affect the user account under which changes were made unless specified otherwise.
3. Is it reversible if I accidentally block a website I need access to?
– Absolutely! Simply remove or comment out the line containing the blocked website in the host file to restore access.
4. Do I need any special technical skills to edit the host file for website blocking?
– Basic familiarity with navigating system files and text editing is helpful, but following step-by-step instructions should be sufficient for most users.
5. Are there any risks involved in editing the host file for website blocking?
– While errors can occur when editing system files, as long as you follow instructions carefully and back up important files, there should be minimal risk.
6. Can I revert back to my original host file if needed after making changes?
– Yes, keeping a backup copy of your original host file allows you to easily restore it by overwriting any modifications made.
7. How quickly will changes made in the host file take effect in blocking websites?
– Typically, changes should take effect immediately once saved; however, refreshing browsers or restarting may sometimes be necessary for full implementation.


How to block websites in Windows: Learn simple techniques to restrict access and enhance your productivity. Start mastering your online space now!